Cyclic singly linked list
Requirements
In this sub-project, you will implement two classes:
- Cyclic linked lists: Cyclic_list, and
- Singly linked nodes: Single_node.
A cyclic linked list with three nodes is shown in Figure 1. The empty cyclic linked list is shown in Figure 2.
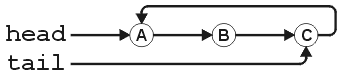
Figure 1. A cyclic linked list and three nodes.
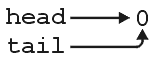
Figure 2. An empty cyclic linked list.
Class Specifications
UML Class Diagram
| Cyclic_list |
|---|
|
- list_head:Single_node - list_tail:Single_node - list_size:Integer |
|
+ create():Cyclic_list + create( in cl:Cyclic_list ):Cyclic_list + size():Integer + empty():Boolean + front():Type + back():Type + head():Single_node + tail():Single_node + count( in obj:Type ):Integer + swap( inout list:Cyclic_list ) + =( in rhs:Cyclic_list ):Cyclic_list + push_front( in obj:Type ) + push_back( in obj:Type ) + pop_front():Type + erase( in obj:Type ):Integer + destroy() |
Description
This class stores a finite list of n (zero or more) elements stored in singly linked nodes. If there are zero elements in the list, the list is said to be empty. Each element is stored in an instance of the Single_node<Type> class. If the list is empty, the head pointer is assigned nullptr. Otherwise, head pointer points to the first node, the next pointer of the ith node (1 ≤ i < n) points to the (i + 1)st node, and the next pointer of the nth node points to the first node.
Member Variables
The three member variables are:
- Two pointers to Single_node<Type> objects, referred to as the head pointer and tail pointer, respectively, and
- An integer referred to as the list size which equals the number of elements in the list.
Member Functions
Constructors
Cyclic_list()
This constructor sets all member variables to 0 or nullptr, as appropriate. (O(1))
Destructor
The destructor must delete each of the nodes in the linked list. (O(n))
Copy Constructor
The copy constructor creates a new instance of the linked list. (O(n))
The copy constructor must create a new cyclicly linked list with a copy of all of the nodes within the copied linked list stored in the same order. Once a copy is made, any change to the original linked list must not affect the copy. (O(n))
Accessors
This class has seven accessors:
- int size() const;
- Returns the number of items in the list. (O(1))
- bool empty() const;
- Returns true if the list is empty, false otherwise. (O(1))
- Type front() const;
- Retrieves the object stored in the node pointed to by the head pointer. This function throws a underflow if the list is empty. (O(1))
- Type back() const;
- Retrieves the object stored in the node pointed to by the tail pointer. This function throws a underflow if the list is empty. (O(1))
- Single_node<Type> *head() const;
- Returns the head pointer. (O(1))
- Single_node<Type> *tail() const;
- Returns the tail pointer. (O(1))
- int count( Type const & ) const;
- Returns the number of nodes in the linked list storing a value equal to the argument. (O(n))
Mutators
This class has six mutators:
- void swap( Cyclic_list & );
- The swap function swaps all the member variables of this linked list with those of the argument. (O(1))
- Cyclic_list &operator=( Cyclic_list & );
- The assignment operator makes a copy of the argument and then swaps the member variables of this cyclic linked list with those of the copy. (O(nlhs + nrhs))
- void push_front( Type const & );
- Creates a new Single_node<Type> storing the argument, the next pointer of which is set to the current head pointer. The next pointer of the last node in the list are also set to the new node. If list was originally empty, the next pointer of the new node is set to itself as is the tail pointer. (O(1))
- void push_back( Type const & );
- Similar to push_front, this places a new node at the back of the list. (O(1))
- Type pop_front();
- Delete the node at the front of the linked list and, as necessary, update the head and tail pointers and the next pointer of any other node within the list. Return the object stored in the node being popped. Throw an underflow exception if the list is empty. (O(1))
- int erase( Type const & );
- Delete the first node (from the front) in the linked list that contains the object equal to the argument (use == to to test for equality with the retrieved element). As necessary, update the head and tail pointers and the next pointer of any other node within the list. Return the number of nodes that were deleted. (O(n))
