Assumptions
This method is based on the assumption that any function with continuous partial derivatives looks like an n dimensional plane. For example, Figure 1 zooms in on a two-dimensional function with continuous partial derivatives. While the function looks reasonably wild, as you zoom in on the red dot, the function looks more and more like a flat plane.
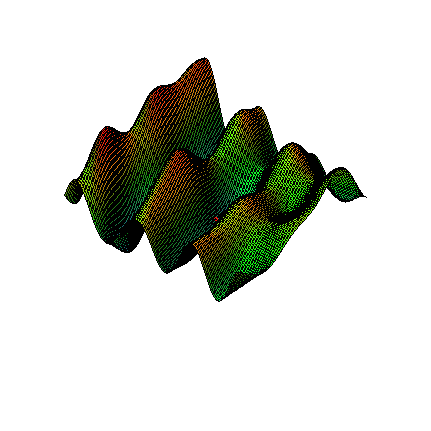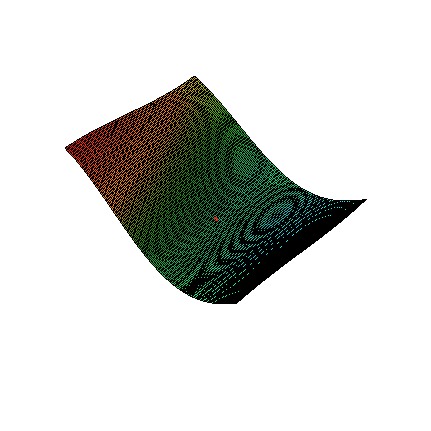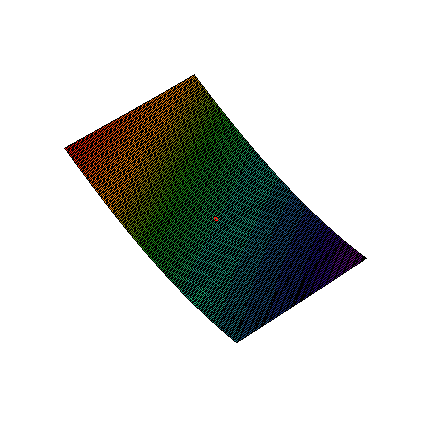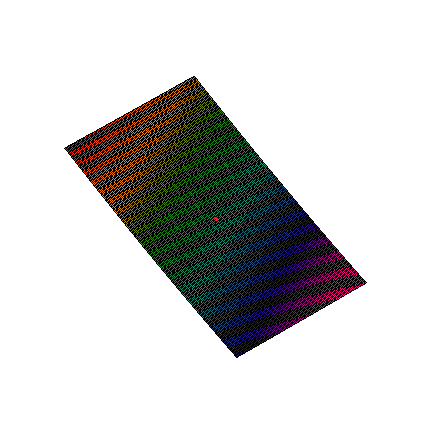
Figure 1. Zoom on a function of two variables.
Similar to Newton's method in one dimension, we will assume that each of the n functions which make up f(x) have continuous partial derivatives which we can compute.
Partial Derivation
To be filled later.
Copyright ©2005 by Douglas Wilhelm Harder. All rights reserved.


